The Pan American Highway: The Longest Road In The World
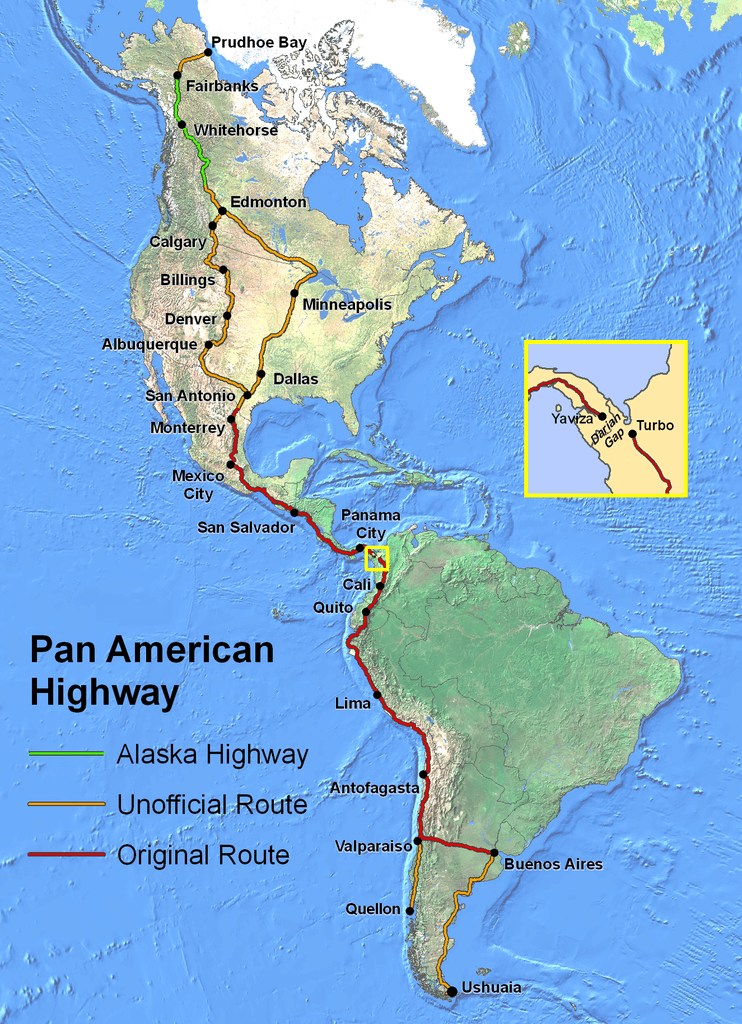
At its fullest extent the Pan-American Highway is a network of roads stretching from Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, to Ushuaia, Argentina, a distance of around 48,000 kilometres (30,000 miles).
According to Guinness World Records, the Pan-American Highway is the world’s longest “motorable road”. However it is not readily possible to drive all the way since the route is interrupted by the 160 kilometre-wide (100 mile) Darién Gap between Central and South America.
The Highway consists of both official and unofficial elements. The official section, which is referred to in Spanish variously as the Autopista / Carretera / Ruta Panamericana, runs from Nuevo Laredo, Mexico on the U.S. Border to Buenos Aires, the capital of Argentina.
However, as shown on the map there are extensive unofficial sections to both the north and south of this.
The route shown on the map runs through 14 countries:
- The United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Guatemala
- El Salvador
- Honduras
- Nicaragua
- Costa Rica
- Panama
- Colombia
- Ecuador
- Peru
- Chile
- Argentina
It also has links to a number of other countries. In the process it passes through all the major climate zones and many varied landscapes including arctic tundra, boreal forest, mountains, prairies, arid deserts and tropical jungles.
Moving from north to south, the route starts at Deadhorse, Alaska near the Prudhoe Bay oilfields and for the first 662 kilometres (414 miles) follows the Dalton Highway to Fairbanks.
The Dalton Highway was constructed in 1974 as a supply road to support the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. It is a challenging drive, with no services of any kind on one 384 kilometre (240 mile) stretch, and was the first road to be featured in the BBC’s World’s Most Dangerous Roads.
From Fairbanks there is a 155 kilometre (96 mile) link to Delta Junction at the northern end of the Alaska Highway, the next part of the route.
The Alaska Highway was constructed in 1942 by the US Army Corps of Engineers, as a wartime project using around 10,000 troops. Its purpose was to link Alaska with the 48 contiguous states through Canada to help defend against a possible Japanese attack.
It was originally around 2,700 kilometres long but as of 2012 had been shortened to 2,232 kilometres (1,387 miles) and is now paved over its entire length.
The Alaska Highway terminates at Dawson Creek, B.C. from where the route shown continues to Edmonton, Alberta. After Edmonton the map identifies two possible routes.
The first goes through Minneapolis after which it follows the Interstate 35 through Dallas/Fort-Worth to the Mexican border at Laredo, Texas.
The second route runs through Calgary, Alberta and Billings, Montana and then connects with the Interstate 25 through Denver, Colorado to Las Cruces, New Mexico and from there on the Interstate 10 to San Antonio, Texas, where it joins the first route.
In practice, given the unofficial status of the routes through Canada and the United States, many other alternatives are possible.
The Mexican city of Nuevo Laredo, just across the border from Laredo marks the start of the official section of the Pan-American Highway.
From there it runs to Mexico City along Mexican Federal Highway 45 and on to the border with Guatemala along Mexican Federal Highway 190.
It then proceeds through Central America, passing through Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. With the exception of Honduras, its route takes it through the capital cities of each of these countries, namely:
- Guatemala City (Guatemala)
- San Salvador (El Salvador)
- Managua (Nicaragua)
- San José (Costa Rica)
- Panama City (Panama)
One of the most challenging sections of the route lies in Costa Rica, where it rises to 3,335 metres (10,942 feet) at the ominously named Summit of Death (Cerro de la Muerte).
This summit marks the highest elevation on the Pan-American Highway in Central America. Indeed, following the completion of the Christ the Redeemer Tunnel between Chile and Argentina (see below), it may well be the highest elevation along the entire route.
The route through Central America terminates abruptly at Yaviza, at the edge of the Darién Gap and resumes on the other side at Turbo, Colombia in South America.
All but the most intrepid circumvent the Gap by taking one of the ferries that go from Panama to Colombia or Ecuador, from where they can reconnect with the Pan-American Highway.
In Colombia the route runs through Medellin and Cali before crossing the border into Ecuador at Tulcán.
In Ecuador the highway goes through the capital, Quito. At 2,850 metres (9,350 feet) Quito is the world’s second highest capital city, exceeded in elevation only by La Paz, Bolivia. From there the route heads south to Peru, where it follows Peru Highway 1, which runs the length of the country and connects all major cities in the coastal area, including the capital, Lima.
On crossing from Peru into Chile the highway enters the Atacama Desert, the driest non-polar location in the world. The highway then follows Chile Route 5 through Antofagasta to Valparaiso.
As shown on the map, there is an unofficial branch of the highway that continues on down the Chilean coast on Route 5 terminating in Quellón on Chiloé Island.
At Valparaiso the official route heads east following Chile Route 60 across the Andes Mountains to Argentina, where it becomes Argentina National Route 7 and crosses the Pampas to Buenos Aires.
Before 1980, the border used to be at the Upsallata Pass, which at 3,832 metres (12, 572 feet) made it the highest point on the Pan-American Highway. However, 1980 saw the opening of the Christ the Redeemer Tunnel (Túnel Cristo Redentor) at 3,200 metres (10,499 feet), which became the new crossing point.
The final (unofficial) leg of the Pan-American Highway runs for 3,045 kilometres (1,892 miles) from Buenos Aires on Argentina National Route 3 to Ushuaia passing through Bahía Blanca and Comodoro Rivadavia.
Near its southern end the route goes back into Chile and crosses the Straits of Magellan via a short ferry ride before going back into Argentina and on to Ushuaia, which is located on Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, the largest island of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago.
Argentina claims Ushuaia as the world’s most southerly city, a fact that is disputed by Chile which claims Puerto Williams for this distinction. While the Chilean town of Puerto Williams is indeed farther south, Ushuaia has a much larger population (71,000 vs. 3,000), so take your pick.
The record for the fastest trip by car from Ushuaia to Prudhoe Bay (mostly on the Pan-American Highway) is credited to Tim Cahill and Garry Sowerby in the astonishing time of twenty-three days, twenty-two hours, and forty-three minutes.
Tim wrote about his experience in his book Road Fever. In 2003 Kevin Sanders broke the Guinness World Record for the fastest traversal of the highway by motorcycle, taking 34 days.
No account of the Pan-American Highway would be complete without a discussion of its missing link, the Darién Gap.
This area of undeveloped swampland, forest and mountain straddles the border between Panama and Colombia. Thus far, plans to build a road through the Gap have come to nothing.
There are a number of reasons for this including:
- The sheer difficulty and cost of building a road through such difficult terrain.
- Pressure to protect the rainforest environment
- Concerns by indigenous groups, such as the Embera-Wounaan and Kuna that a road would pose a threat to their traditional cultures.
- And concerns that a road would make it easier for foot and mouth disease to enter North America.
Over the years, the enormous challenge of traversing the Gap has attracted a number of diehard souls.
The first vehicular crossing of the Gap was by the Land Rover La Cucaracha Cariñosa (The Affectionate Cockroach) and a Jeep of the international Trans-Darién Expedition of 1959–60, which took 136 days!
The first crossing by a standard two wheel drive passenger car took place in 1961 with three Chevrolet Corvairs, only two of which made it out of the jungle.
Up to this point, the expeditions had used river boats for some sections. The first fully overland wheeled crossing of the Gap was that of British cyclist Ian Hibell, who rode from Cape Horn to Alaska between 1971 and 1973.
The first motorcycle crossing was by Robert L. Webb in March 1975.
The first all-land auto crossing was in 1985–87 by Loren Upton and Patty Mercier in a Jeep, taking an incredible 741 days to travel 201 kilometres (125 miles).
Ed Culberson was the first to follow the entire Pan-American Highway including the Darién Gap on a motorcycle.
There have also been a number of crossings on foot, including that of George Meegan in 1981, who walked the entire distance from Tierra del Fuego to Alaska over a period of 2,425 days!
The most unusual walker was evangelist Arthur Blessitt who traversed the Gap in 1979 while carrying a 12-foot wooden cross as part of what Guinness World Records recognized as “the longest round the world pilgrimage”.
Principal References:
Books:
Tim Cahill, Road Fever (1991)
Ed Culberson, Obsessions Die Hard: Motorcycling the Pan-American Highway’s Jungle Gap (1966)
George Meegan, The Longest Walk (1988)
Russell Braddon, The Hundred Days of Darien (1974)
John Blashford-Snell, Something Lost Behind the Ranges (1994)
Ian Hibell, Into the Remote Places (1984)
Mark A Smith, Driven by a Dream (2004)
Wade Davis, The Rucksack Man (1976)
Arthur Blessitt, The Cross (2009)
Joseph R. Yogerst, Long Road South: The Pan American Highway (1999)
Raymond and Audrey Pritchard, Driving the Pan-American Highway to Mexico and Central America (1998)
Brad and Sheena Van Orden, Drive Nacho Drive: A Journey from the American Dream to the End of the World (2013)
Ben Cunningham, The Longest Road: An Irish Pan-American Cycling Adventure (2009)
Enjoy this post? Then please help us by sharing it:






